Everything about High-Speed Data Transfer in 2025
August 15, 2024
High-speed data transfer is essential in today's digital world. From global file sharing to streaming HD content, speed matters. This post explores factors affecting transfer speeds and top solutions. Learn how to optimize your data transfer and overcome frustrating delays.
What Is High-Speed Data Transfers
High speed data transfer refers to the process of moving large amounts of data quickly from one place to another. Whether you're sending files across a local network, sharing documents with a colleague halfway around the world, or backing up your data to the cloud, high speed file transfer ensures that this happens efficiently, saving you time and reducing frustration.
But what exactly makes a data transfer "high-speed"? It comes down to how quickly data can be transmitted between devices or over networks. This speed is influenced by various factors like network bandwidth, latency, and the protocols used to manage the transfer.
Key Factors Affecting Data Transfer Speed
When it comes to high speed data transfer, several key factors determine just how quickly your files will move from point A to point B. Think of it like a race car on a track—everything from the car's engine (network bandwidth) to the smoothness of the road (latency) impacts its speed.
Here are some of the key factors that can affect your data transfer speed:
1. Network Bandwidth
Network bandwidth is like the width of the highway your data travels on. The broader the highway, the more data can pass through at once, leading to faster transfers.
Bandwidth is typically measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). Higher bandwidth allows for more data to be transferred simultaneously, which is crucial when dealing with large files or a high volume of smaller files.
However, just like a highway, if too many cars (or too much data) try to squeeze through at once, traffic jams (or slow transfer speeds) can occur. To maximize your data transfer speed, ensuring you have sufficient bandwidth is key—whether that means upgrading your internet plan or optimizing your network infrastructure.
2. Latency
Latency is the time delay that occurs as data travels from its source to its destination. Imagine sending a text message and waiting for the reply, the time it takes for that reply to come back is akin to latency in data transfer.
Low latency means data travels quickly, while high latency causes delays, like waiting for a sluggish response. This delay can be influenced by the physical distance between devices, the quality of the network, and even the type of cables used. For high-speed file transfers, minimizing latency is crucial.
Techniques like using fiber-optic cables, optimizing network routes, and reducing the number of "hops" (intermediary steps) your data takes can all help in lowering latency, making your transfers faster and more efficient.
3. Packet Loss
Packet loss occurs when some of the data packets being transferred don't make it to their destination.
Imagine sending a letter, but some words or sentences disappear during the journey—frustrating, right? In data transfer, packet loss can slow down the process significantly, as missing packets often need to be retransmitted, causing delays.
Packet loss can be caused by network congestion, faulty hardware, or poor network configurations. To minimize packet loss, it's essential to have a stable network, use reliable hardware, and avoid overloading your network with too much data at once. By keeping packet loss to a minimum, you ensure a smoother and faster transfer experience.
4. Protocol Used
The protocol used for data transfer is like the rules of the road for your data. Different protocols govern how data is sent, received, and verified, impacting the overall speed of the transfer.
For example, TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is reliable and ensures that all data arrives correctly, but it can be slower due to its error-checking processes.
On the other hand, UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is faster because it skips some of these checks, though it may result in occasional errors. Choosing the right protocol for your needs—whether it's speed, reliability, or a balance of both—can make a significant difference in your high-speed data transfer efforts.
Top 4 High-Speed Data Transfers Recommended
When speed is of the essence, not all high speed data transfer software for pc or high speed file transfer apps are created equal.
Whether you're moving massive files across continents or sharing important documents within your office, choosing the right high-speed data transfer solution can make all the difference. Let's look at four top-tier options for high-speed data transfers in 2025.
1. Raysync
Raysync is a leading high-speed file transfer solution designed to handle large-scale data movement efficiently and securely. With its proprietary transfer protocol, Raysync accelerates file transfers by optimizing bandwidth usage and minimizing latency.
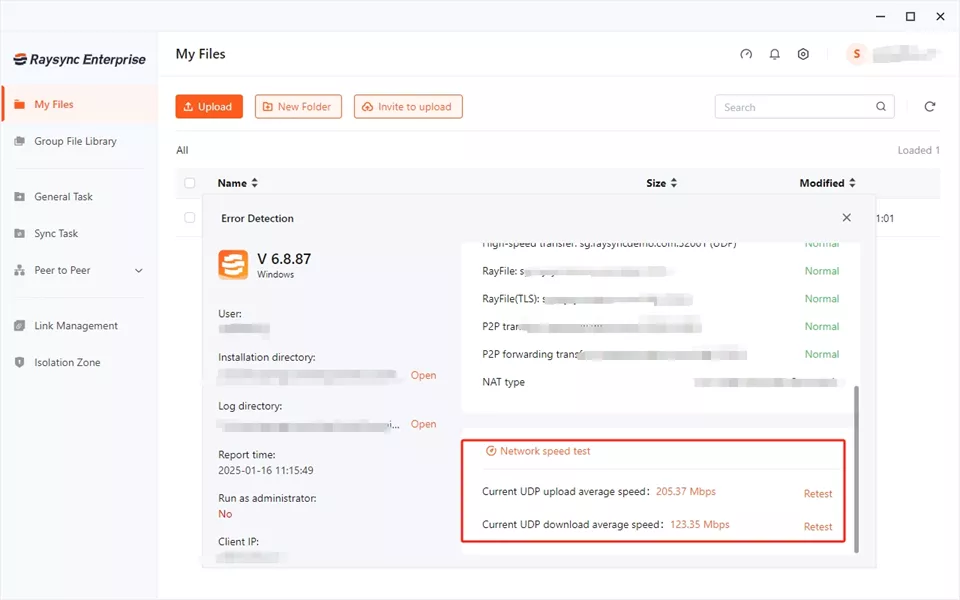
It supports a wide range of file types and sizes, making it ideal for industries like media, entertainment, and finance that deal with massive data volumes. What sets Raysync apart is its ability to handle complex transfers with ease, providing robust security features and detailed transfer management tools that give users complete control over their data.
Pros:
- Raysync's main advantage lies in its speed and reliability, especially over long distances.
- The software is highly scalable, catering to businesses of all sizes.
- It has a user-friendly interface, which simplifies even the most complex transfers.
Cons:
- The initial setup can be somewhat challenging for less tech-savvy users.
- The brand is relatively new in the market.
Free Trial Policy: Raysync offers a 15-day free trial with access to all major functionalities.
2. Aspera
IBM Aspera is a well-established name in the world of high speed data transfer. Known for its cutting-edge FASP (Fast Adaptive Secure Protocol) technology, Aspera revolutionizes the way data is moved across the globe.
It excels in environments where traditional transfer methods struggle, particularly when dealing with high-latency networks or vast amounts of data.
Aspera is widely used in industries such as media, gaming, and healthcare, where the need for speed and security is paramount. Its ability to transfer data at maximum speed regardless of file size, distance, or network conditions makes it a preferred choice for many.
- Pros:
Aspera's greatest strength is its unmatched transfer speed, even in challenging network conditions. - The software is highly secure, ensuring that sensitive data is protected during transit.
Cons:
- Aspera can be complex to set up and use, particularly for those unfamiliar with advanced data transfer protocols.
- The pricing can be a bit challenging for small businesses looking for high speed file transfer app.
Free Trial Policy: Aspera offers a 30-day free trial, allowing users to test out its high-speed transfer capabilities.
3. Signiant
Signiant is another powerhouse in the high speed data transfer arena, offering cloud-native solutions that are designed for media and entertainment industries. Signiant's intelligent transport technology enables fast, secure, and reliable file movement, whether it's within a single organization or across the globe.

One of Signiant's standout features is its ability to scale seamlessly from small files to multi-terabyte data sets, all while maintaining speed and efficiency. Signiant also integrates well with cloud storage solutions, making it a versatile choice for companies looking to optimize their data workflows.
- Pros:
The major advantage of Signiant is its scalability and flexibility, which makes it suitable for businesses of all sizes. - Its intuitive interface and seamless cloud integration are also strong points.
Cons:
- Signiant's pricing structure can be complex.
- Its cost can quickly add up, especially for larger operations.
- While the software is solid, it may require a bit of a learning curve for new users.
Free Trial Policy: Signiant offers a 14-day free trial, giving users a chance to explore its features and assess its performance.
4. FileCatalyst
FileCatalyst is a high speed data transfer software for pc known for its ability to accelerate large data transfers, making it a favorite among industries that regularly deal with big data. Utilizing UDP-based technology, FileCatalyst overcomes the limitations of traditional TCP-based transfers, delivering speeds that are up to hundreds of times faster.

It's designed to handle the demands of modern data environments, providing a range of deployment options including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid models. FileCatalyst is particularly popular in sectors like broadcasting, oil and gas, and scientific research, where time-sensitive data transfer is critical.
Pros:
- FileCatalyst's strength lies in its speed and versatility, offering multiple deployment options to fit different organizational needs.
- It's also highly reliable, with built-in mechanisms to ensure data integrity during transfers.
Cons:
- The software's advanced features may be overkill for smaller businesses or those with simpler data transfer needs.
- While it's packed with features, the learning curve can be steep, and the cost may be a concern for budget-conscious organizations.
Free Trial Policy: FileCatalyst offers a 30-day free trial, giving users ample time to test its high-speed transfer capabilities.
FAQs about High-Speed Data Transfer
When it comes to high speed data transfer, questions are bound to arise. Here are the answers to some of the most common questions about data transfer speeds, media, and methods:
1. What is the fastest possible data transfer speed?
The fastest possible high speed data transfer depends on several factors, including the technology used, network conditions, and the type of data being transferred. In ideal conditions, fiber-optic connections can achieve speeds up to 100 Gbps (Gigabits per second).
However, real-world conditions often limit these speeds due to latency, network congestion, and other factors. For businesses seeking to maximize their transfer speeds, solutions like Raysync offer advanced protocols that optimize bandwidth usage and minimize latency, ensuring you get the fastest possible transfer speeds under varying conditions.
2. Which is the fastest media for data transfer?
When it comes to the fastest media for data transfer, fiber-optic cables take the lead. Fiber optics use light to transmit data at incredible speeds, making them far superior to traditional copper cables. This technology can support data transfer rates of up to 100 Gbps and beyond, depending on the setup.
Fiber optics are commonly used in high-speed internet connections and enterprise networks where large volumes of data need to be transferred quickly and reliably. For those looking for high-speed data transfer solutions, leveraging fiber-optic infrastructure combined with advanced software like Raysync can provide unparalleled speed and efficiency, making it the go-to choice for modern data transfer needs.
Conclusion
High-speed data transfer is crucial in today's digital age. Tools like Raysync maximize network potential for lightning-fast transfers. To achieve optimal speed, focus on bandwidth, low latency, and efficient protocols. Enjoy the benefits of smooth, efficient data transfer!
You might also like

Industry news
April 17, 2025Looking for the best way to transfer large files over Internet in 2025? Explore top methods for individuals and businesses, including cloud storage, file transfer services, and P2P tools.
![How to Send 4K Video to Someone [Personal/Studio]](http://images.ctfassets.net/iz0mtfla8bmk/2FTbUvTilN05irU2fHXIjy/6f7df0216ffad8cedf60d252f76e51f6/how-to-send-4k-video-to-someone.png)
Industry news
June 21, 2024Learn how to send 4K video to someone without losing quality. Tips for sending 4K videos in high quality.

Industry news
September 19, 2024Discover everything about FTPS file transfer, how it works, top enterprise applications, and faster FTPS transfer alternatives like Raysync for secure and efficient data transfers.